Europe's Drying Landscape: A Call to Action

Drought, once considered a sporadic natural event, is evolving into a persistent and escalating crisis across Europe. Prolonged periods of insufficient rainfall are creating water stress and are straining ecosystems, agriculture, and economies, with far-reaching consequences.
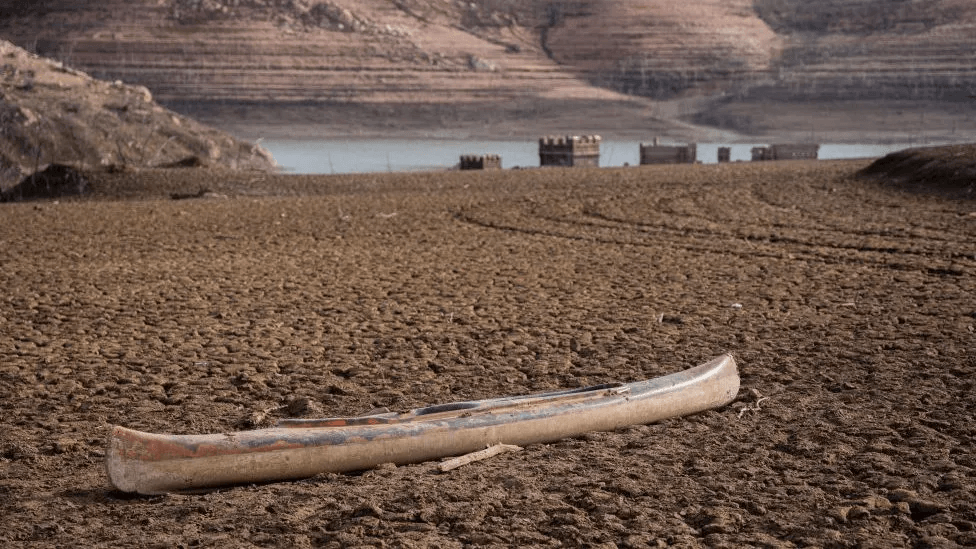

The Sau reservoir reached its lowest level on record in January (BBC getty images)
Understanding Drought and Water Stress
Drought and water scarcity are distinct but interconnected phenomena. While drought refers to a temporary decrease in water availability, water scarcity is a more chronic condition where demand consistently outpaces supply. While these conditions are natural, the frequency and severity of droughts is likely to be intensified by climate change.
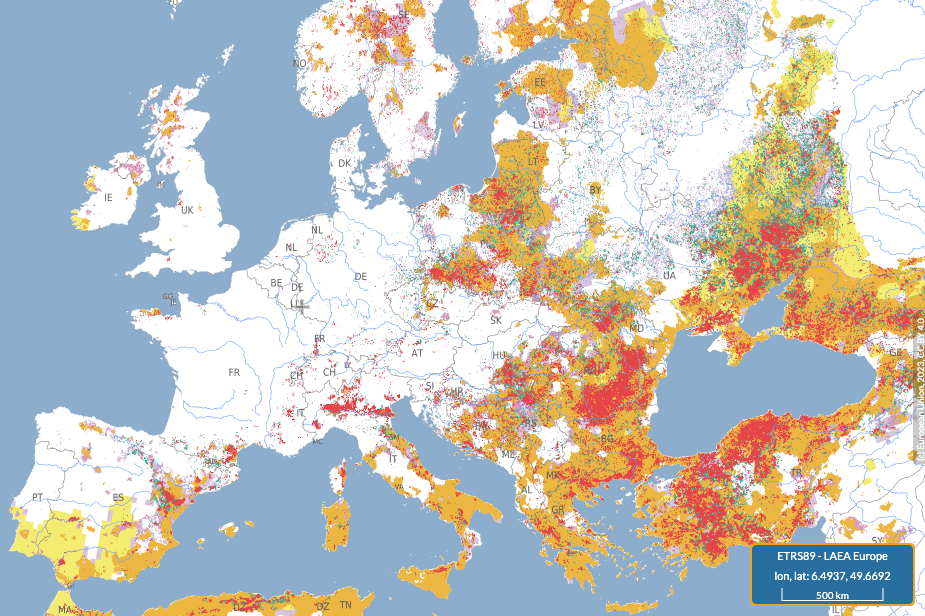
Combined Drought Indicator for Europe in July 2024 from European Drought Observatory.
The Economic Toll of Drought
Drought is a growing economic crisis. The current economic toll in the EU is already substantial, about €9 billion in damages annually. With a 3°C global warming by 2100, drought losses in Europe could be five times higher than today, with the Mediterranean and Atlantic regions facing the most severe impacts.
Drought's far-reaching consequences span agriculture, energy, and industry. Crop failures, reduced yields, and livestock losses devastate rural communities. The energy sector grapples with decreased hydropower generation and increased cooling water demands. Water scarcity also threatens industries reliant on water for production, such as manufacturing and food processing.
Southern Europe: A Hotspot for Drought
Southern Europe is emerging as a hotspot for drought, with cascading impacts on its economies and ecosystems. Catalonia, Spain, is a stark example of this crisis, facing its worst drought on record in February this year. Some areas have endured over three years without rain, forcing severe water restrictions on millions. The agricultural sector, particularly reliant on water-intensive crops, has been crippled, with farmers facing an 80% water consumption cut.
The Rise of Megadroughts
A particularly alarming trend is the emergence of megadroughts, characterized by their extensive geographic scope and prolonged duration. The 2022 European drought, impacting over 630,000 km² and causing river flows to drop below average in nearly two-thirds of the continent, serves as a stark example. These events pose significant threats to food security, water supply, and energy production, as evidenced by widespread crop failures, water shortages, and reduced hydropower generation during this period.
Cascading Climate Risks
Drought is not an isolated issue but part of a complex web of interconnected climate risks. For example, droughts can exacerbate wildfires, leading to further environmental and economic damage. Accounting for these cascading effects is crucial for developing effective adaptation strategies.
The Urgent Need for Action
The growing threat of drought underscores the imperative for urgent and comprehensive action. Investing in water-efficient technologies, improving water management practices, and diversifying water sources are essential steps. Additionally, early warning systems and robust drought monitoring and assessment are vital for effective response and mitigation.
refinq is committed to helping organizations navigate the challenges posed by drought and water stress in changing climate. Our innovative climate risk assessment tool provides crucial insights into potential drought and water stress impacts on your business operations. By leveraging the latest climate science, we empower you to proactively prepare for water scarcity and its associated challenges. Partner with us to proactively manage climate risks and build a more resilient future.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you.
References:
- https://water.europa.eu/freshwater/europe-freshwater/freshwater-themes/drought
- https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/european-climate-risk-assessment
- https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/indicators/drought-impact-on-ecosystems-in-europe
- https://www.dw.com/en/spain-catalonia-declares-drought-emergency-for-barcelona/a-68143732
- https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2023/apr/20/frightening-record-busting-heat-and-drought-hit-europe-in-2022
Cover Image: Pixabay on Pexels